mechanical properties of soil
2019-07-21T15:07:52+00:00

Mechanical Properties of Soils Hunker
Mechanical Properties of Soils Shear Strength Shear strength refers to the level of shear stresses a material can resist without fracture Shear Lateral Earth Pressure Lateral earth pressure is the pressure that earth exerts horizontally If you have a cubic mass Consolidation Consolidation Mechanical properties of soil Distribution of vertical and horizontal stresses in the soil with calculation methodMechanical properties of soil Distribution of vertical Plants with roots obtain nutrients and moisture from soil through their roots Soils are characterised by their physical, chemical and biological properties In addition, soils are good materials(PDF) Engineering Properties of Soils

The types and the properties of the soil Science online
The silt soil properties The colour of the silt soil is grey The size of its particles is medium (between the sand soil particles and the clay soil particles It is moderately aerated soil that has medium absorption of the waterSurface area of soil affects its physical and chemical properties and is largely determined by amount of clay present in soil: Specific surface area of soil particles Effective Area Specific Surface Area Particle Diameter (cm) Mass (g) (cm2) (cm2g1) Gravel 2 x 101113 x 10213 x 101111 Sand 5 x 103177 x 10779 x 1054444 Silt 2 x 104113 x 101113 x 107111 x 104CHAPTER 1 SOIL PHYSICAL PROPERTIESThe test results show some changes, negligible in some cases, on the mechanical properties of the soils treated with Conaid Also, both Standard and Modified Proctor compaction tests show negligible or even negative effects on maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of test soils except for kaolinite However, no significant, consistent increases in the shear strength are observed Mechanical Characteristics of Soils ERA

WHAT ARE THE ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF SOIL?
Engineering Properties of Soil The following properties of soil are taken into consideration while dealing with soil as a construction material Cohesion Angle of internal friction Capillarity Permeability Elasticity Compressibility 1 Cohesion It is the internal molecular attraction which resists the rupture or shear of a material Cohesion is derived in the fine grained soils [] Soil is traditionally solidified with lime Limesoil has better properties in improving the strength , , , but it is characterized with poor tensile strength and strong cracking As a further improvement, fibers are added into limesoil to enhance the mechanical properties, and to reduce the vertical and lateral deformation , , Mechanical properties of soil reinforced with both lime The knowledge of soil mechanics has application in many fields of Civil Engineering 1 Foundations The loads from any structure have to be ultimately transmitted to a soil through the foundation for the structure Thus, the foundation is an important part of a structure, the type and details of which can be decided upon only []APPLICATIONS OF SOIL MECHANICS The Constructor

CHAPTER 1 SOIL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
soil properties Soil Texture Classification: Soil separate equivalent diameter size (mm) gravel > 2 mm Sand 005 2 mm very coarse 1 2 mm coarse 05 1 mm medium 025 05 mm fine 01 025 mm very fine 005 01 mm Silt 0002 005 mm Clay 005 mm 2 Sedimentation Stokes’ law, if Request PDF Mechanical properties of structured unsaturated soils The strength of structured soils during loading depends on effective as well as on neutral stresses Differences in the Mechanical properties of structured unsaturated soils Soil consistence is defined, another way, as the physical condition of the soil at various moisture content as evidenced by the behaviour of that soil toward mechanical stresses or manipulation The two forces responsible for soil consistence are cohesion and adhesion which act within the soilList of Physical Properties of Soil Soil Science

Structure characteristics and mechanical properties of
Soils with a higher degree of EF flocculation due to the prevailing Coulombian or van der Waals attraction can render a higher liquid limitKey words: pH, fabric associations, isoelectrical point, dual porosity, interparticle forces, liquid limitChapter 5 Engineering Properties of Soil and Rock 51 Overview The purpose of this chapter is to identify, either by reference or explicitly herein, appropriate methods of soil and rock property assessment, and how to use that soil and rock property data to establish the final soil and rock parameters to be used for geotechnical design The final properties to be used for design should be Chapter 5 Engineering Properties of Soil and RockSoil Properties and the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) George E Thomas, PE A Identification and Classification 1 General Most soils are a heterogeneous accumulation of mineral grains that are not cemented together However, the term "soil" or "earth" as used in engineering includes virtually every type of uncemented or partially cemented inorganic and organic material in the Soil Properties and the Unified Soil Classification System

Mechanical Characteristics of Soils ERA
The test results show some changes, negligible in some cases, on the mechanical properties of the soils treated with Conaid Also, both Standard and Modified Proctor compaction tests show negligible or even negative effects on maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of test soils except for kaolinite However, no significant, consistent increases in the shear strength are observed Soil Physical (Mechanical) Properties ; Bulk density, porosity, strength, consistency; 2 Definitions Atterberg limits (H Matengu) Soil strength (L Olver) Soil dynamics (N Davenport) Soil micromorphology (A Pietersen) 3 Physical properties ; Characteristics of soil which can be measured by physical means and expressed in physical terms, such as colour, density, porosity, hydraulic PPT – Soil Physical (Mechanical) Properties PowerPoint Soils with a higher degree of EF flocculation due to the prevailing Coulombian or van der Waals attraction can render a higher liquid limitKey words: pH, fabric associations, isoelectrical point, dual porosity, interparticle forces, liquid limitStructure characteristics and mechanical properties of

Properties of Soil Engineersdaily Free engineering
Soil mechanics has become a distinct and separate branch of engineering mechanics because soils have a number of special properties, which distinguish the material from other materials Its development has also been stimulated, of course, by the wide range of applications of soil engineering in civil engineering, as all structures require a sound foundation and should transfer its loads to the Studies in the physical properties of soils: I Mechanical properties concerned in cultivation Volume 15 Issue 2 William B HainesStudies in the physical properties of soils: I Mechanical Soil consistence is defined, another way, as the physical condition of the soil at various moisture content as evidenced by the behaviour of that soil toward mechanical stresses or manipulation The two forces responsible for soil consistence are cohesion and adhesion which act within the soilList of Physical Properties of Soil Soil Science

Mechanical properties and stress–dilatancy relationships
However, there are few studies investigating mechanical properties of unsaturated soils under cyclic loadings There are two objectives in this paper One objective is to investigate cyclic properties of an unsaturated silt under various cyclic loading conditions, while the other is to investigate the stress–dilatancy relationships; the relation of plastic strain increment ratio, de v p Physical properties of soil include color, texture, structure, porosity, density, consistence, temperature, and air Colors of soils vary widely and indicate such important properties as organic matter, water, and redox conditions Soil texture, structure, porosity, density, and consistence are related with types of soil particles and their arrangement There are two types of soil particles Physical Properties of Soil SpringerLinkIn Demonstration 2, students examine soil properties such as soil horizons, texture, structure, color, depth, and pH in a large soil pit Students and the instructor discuss how the soil properties observed affect the use of the soil for farming, gardening, and other purposes > SUPPLEMENTAL DEMONSTRATIONS AND EXAMPLES (1 HOUR) These simple demonstrations offer ideas for using 21 Soils and Soil Physical Properties

Geotechnical properties of soils SlideShare
Sometimes these are called as geotechnical properties 5 5 1 Soil texture and soil structure: Both are unique properties of the soil that will have a profound effect on the behavior of soils 2 Specific Gravity : The specific gravity of soil, Gs, is defined as the ratio of the unit weight of a given material to the unit weight of water 6 6
- mill digunakan rol vertikal
- iron ore double roll saudi gold crusher made in brazil for sale
- vibrating screener technical data
- tentara batu menghancurkan peralatan di vietnam
- gold processing plants for hire in south africa
- OPEN PIT MINE PLANNING AND DESIGN TWO VOLUME SET ROUTLEDGE
- gambar dan prinsip kerja gyratory crusher
- of pulverizer manufacturer in india
- ncrete crushing equipment jaw crusher
- gold ore mechanical seperation
- metal shredder reject door factory
- ncentration of magnetic separation
- wet stones for sharpening knives
- Cyanite Mobile Crusher Price For Sale
- grinding machine for small scale iron mining
- podiatrist drum sander
- lling system for gypsum kiln
- increase arse aggregate crusher
- eguipment for gold mining sale in ghana
- ashoka roller flour mills in delhi
- picture showing mining operation chromite sand
- INTRODUCTION TO WIND TURBINE COUPLINGS
- iron ore crusher production line
- Hubei Mining Equipment
- pf 1214 feldspar impact crushers
- crush power orden de bandas
- grinder and quarry plant in philippines
- quartz crusher for gold searching
- grinding equipment
- italy granitet machine mpany India crusher
-

Primary mobile crushing plant

Independent operating combined mobile crushing station

Mobile secondary crushing plant

Fine crushing and screening mobile station

Fine crushing & washing mobile station

Three combinations mobile crushing plant

Four combinations mobile crushing plant
-

HGT gyratory crusher

C6X series jaw crusher

JC series jaw crusher

Jaw crusher

HJ series jaw crusher

CI5X series impact crusher

Primary impact crusher

Secondary impact crusher

Impact crusher

HPT series hydraulic cone crusher

HST hydraulic cone crusher

CS cone crusher

VSI6S vertical shaft impact crusher

Deep rotor vsi crusher

B series vsi crusher
-

Vertical grinding mill

Ultra fine vertical grinding mill

MTW european grinding mill

MB5X158 pendulum suspension grinding mill

Trapezium mill

T130X super-fine grinding mill

Micro powder mill

European hammer mill

Raymond mill
Ball mill
-

GF series feeder

FH heavy vibrating feeder
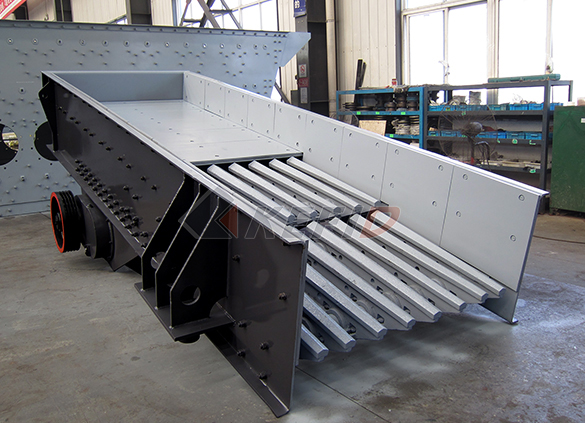

TSW series vibrating feeder
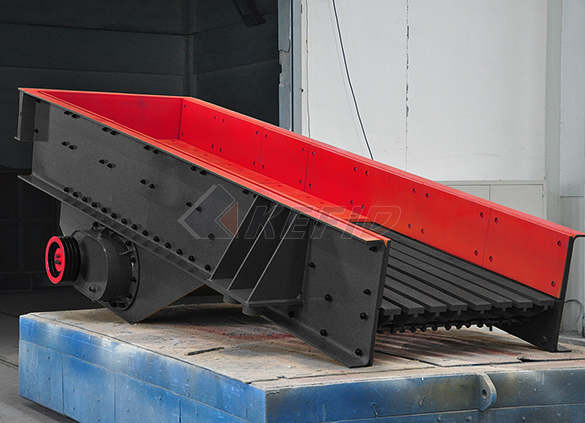

Vibrating feeder
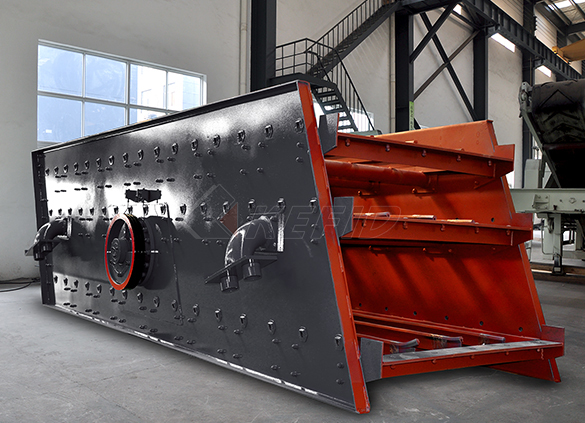

Vibrating screen
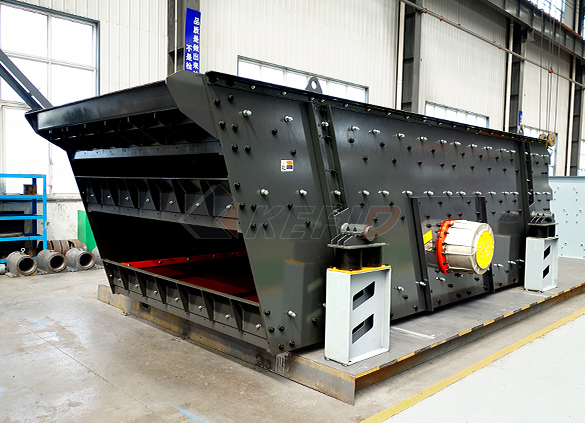

S5X vibrating screen

Belt conveyor

Wheel sand washing machine

Screw sand washing machine

