hazards and risks in mining
2022-03-27T05:03:06+00:00

Mining health and safety: 7 common risks to protect
A common health risk that miners face is thermal – or heat – stress “Mining environments are often very hot and humid, particularly those in outback Australia, which over time can cause thermal stress in workers “Overexposure to heat and humidity can cause the body to become fatigued and distressed Ruth’s Top 10 Risks in Mining: Behaviour; Communication; Vehicle Interactions; Explosives; Electricity; Working at Height; Confined Space; Fire; Lifting Objects; Ground Failure; For more information about these mine safety hazards and risks and some practical guidance on how best to control them, Download the full article here: [Download not found] Please share our posts Click to Top 10 Safety Hazards In Mining Safety Risk netCoal mining risks Coal mining has been one of the most common (and dangerous) forms of mining for a number of years Thousands of people have died in coal mines, and hundreds continue to face the safety hazards of mining coalMining risks: Coal, uranium, phosphate, bauxite, iron ore

What are risks associated with mining? Creative Safety
→ Electrical hazards: Most mines have different pieces of electrical equipment used on a regular basis Although necessary, these machines can pose a risk of fire, shock, or arc flash And the cords connected to equipment also pose a trip and fall hazard to workersMining is a hazardous operation and consists of considerable environmental, health and safety risk to miners Unsafe conditions in mines lead to a number of accidents and cause loss and injury to human lives, damage to property, interruption in production etcHAZARD IDENTIFICATION AND RISK ANALYSIS IN MINING → Vehicle hazards: Industrial vehicles like cement trucks, cranes, or tractors can often be found at mining sites These vehicles do not usually offer the best visibility for operators and can put all the workers in the area at risk Ensure workers can be easily spotted with hivis safety vests and take the time to draw out a traffic plan for the areaWhat are risks associated with mining? Creative Safety

Specific and NonSpecific Hazards in Underground Mines
Fires and explosions have been some of the most destructive and dangerous hazards in the mining industry It is also one of the most challenging safety issues that miners face They can occur at any time, whether that's in an active or abandoned facility The document “The prevention and control of fire and explosion in mines” issued by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) lists a number The principal airborne hazards in the mining industry include several types of particulates, Exposure to mercury vapour, and thus risk of mercury poisoning, is a hazard among gold miners and millers and among mercury miners Exposure to arsenic, and risk of lung cancer, occurs among gold miners and lead miners Exposure to nickel, and thus to risk of lung cancer and skin allergies, occurs Health Hazards of Mining and QuarryingThe Need for Risk Management in Mining Risk is inherent in any business, but especially so in mining Tools, as a contractor management system, exist to keep contractors safe and mitigate both the risk to their safety and the risk to your company’s investment potential Safety Management Tools Can Help Indeed, a contractor management system with its evaluation module can identify top Risk Management and Safety in Mining Cognibox

[PDF] Hazard Identification and Risk Analysis in Mining
For any industry to be successful it is to identify the Hazards to assess the associated risks and to bring the risks to tolerable level Mining activity because of the very nature of the operation, complexity of the systems, procedures and methods always involves some amount of hazards Hazard identification and risk analysis is carried for identification of undesirable events that can leads Mining being a hazardous operation has considerable safety risk to miners Unsafe conditions and practices in mines lead to a number of accidents and causes loss and injury to human lives, damages the property, interrupt production etc Risk assessment is a systematic method of identifying and analysing the hazards associated with an activity and establishing a level of risk for each hazard HAZARD IDENTIFICATION AND RISK ANALYSIS IN MINING Environmental hazards are present during every step of the openpit mining process Hardrock mining exposes rock that has lain unexposed for geological eras When crushed, these rocks expose radioactive elements, asbestoslike minerals, and metallic dust During separation, residual rock slurries, which are mixtures of pulverized rock and liquid, are produced as tailings, toxic and radioactive Environmental Risks of Mining

CDC Mining The Application of Major Hazard Risk
Additionally, if a mining operation is not prepared to discuss its major hazards in an open and honest fashion and to present the findings of the risk assessment in a written report, the MHRA output will be unclear, and attempts to monitor or audit important controls may not be possible A MHRA is most effective when the mining operation possesses 1) a proper understanding of its hazards, 2 This project was designed to improve the understanding of the cognitive processes—such as visual search, risk perception, and risk tolerance—involved in successful hazard recognition for SSG mine workers Initial testing took place in NIOSH laboratories Experienced and novice SSG mine workers, SSG mine safety professionals, and mining students participated in the study During data CDC Mining Project Identifying Hazards at Mines NIOSHThe first three issues highlight hazards and risks in the underground mining environment, while the last three reinforce the critical importance of people, training, organizations, systems and structures in improving health and safety in Ontario mines Addressing these issues could significantly improve health and safety outcomes 1 The Internal Responsibility System first appeared in Ontario Mining Health, Safety and Prevention Review

Risk Management and Safety in Mining Cognibox
The Need for Risk Management in Mining Risk is inherent in any business, but especially so in mining Tools, as a contractor management system, exist to keep contractors safe and mitigate both the risk to their safety and the risk to your company’s investment potential Safety Management Tools Can Help Indeed, a contractor management system with its evaluation module can identify top Environmental hazards are present during every step of the openpit mining process Hardrock mining exposes rock that has lain unexposed for geological eras When crushed, these rocks expose radioactive elements, asbestoslike minerals, and metallic dust During separation, residual rock slurries, which are mixtures of pulverized rock and liquid, are produced as tailings, toxic and radioactive Environmental Risks of MiningMine safety is a broad term referring to the practice of controlling and managing a wide range of hazards associated with the life cycle of miningrelated activities Mine safety practice involves the implementation of recognised hazard controls and/or reduction of risks associated with mining activities to legally, socially and morally acceptable levelsMine safety Wikipedia

[PDF] Hazard Identification and Risk Analysis in Mining
For any industry to be successful it is to identify the Hazards to assess the associated risks and to bring the risks to tolerable level Mining activity because of the very nature of the operation, complexity of the systems, procedures and methods always involves some amount of hazards Hazard identification and risk analysis is carried for identification of undesirable events that can leads Critical hazards and controls for highrisk operations will assist mines in making decisions on the most important and effective safety interventions Worksheets, including the controls, management performance standards and daytoday performance measures for both large and small mines are provided for six critical controls: Dropped or Falling Objects Fall from Heights Ground Failure and Critical Risks and Controls Risk Management in Mining Working underground presents a variety of health and safety risks—but recent advances in safety legislation and equipment have produced significant reductions in injuries in the mining industry The key to maintaining worker health and safety lies in prevention But when it comes to many mining sites, there are some issues getting in the way3 Mining Industry Safety Issues – SafeStart

Health hazards in coal mining Australasian Mine Safety
Working in the mining sector obviously comes with risks, however not all the risks are directly linked to the physical side of the job and its dangers There are obvious workplace risks of course, but living near the mines can also pose a range of environmental health concerns and hazards in itself Health hazards in coal mining can be controlled and managed with effective strategies You can Introduction Safety is the prime concern Mining is an hazardous operation Unsafe condition lead to accident Estimation of risk level What is HIRA? 4 Need for risk assessment Level of risk Understanding the hazard Helps to make decision Implementation of safety improvements 5Hazard identification and risk analysis in mining industryThe first three issues highlight hazards and risks in the underground mining environment, while the last three reinforce the critical importance of people, training, organizations, systems and structures in improving health and safety in Ontario mines Addressing these issues could significantly improve health and safety outcomes 1 The Internal Responsibility System first appeared in Ontario Mining Health, Safety and Prevention Review

Hazards identified and the need for health risk assessment
The South African government is committed to controlling the hazards of mining However, there are a number of issues concerning management of the hazards and risks in South African mines Health and safety in mines in South Africa is regulated by the Mine Health and Safety Act 29 of 1996 and the Mine Health and Safety Act regulations The Act
- Rock Crushing Amp Grinding Manufacturer In India
- list of iron ore beneficiation plant worldwide
- chemical reactions during mining
- salary of a manager in barite processing mpany in nigeria
- lime crushing plant dothan us puerto ri
- Grinding Machine Distributor In Indonesia
- of process of crushed limestone
- Spiral Concentration For Iron Ore Upgradation
- INTERNAL DIAGRAM OF ROCK CRUSHER
- Used Gold Mining Equipment South Africa
- crusher plant 500 600tph
- roller grinding machine jiangsu tianma china
- vertical roller mill operation and parameters
- in which industry jaw crusher is used
- vibrating machine for ore dividing
- prices for m sand washer on sale in india
- строительный песок стиральная машина
- iron ore beneficiation processing plant for sale iron ore
- crusher run machine in malaysia
- ncrete crusher specifi ions water nsumption
- dimensional analysis and ball mill performance
- much how much st a mobile batch plant
- how much does a ballast crushing machine st
- material crushing machine
- grinding of pper in industry
- stone crusher plant and its
- fine ultra fine grinding mill in russia
- weight restriction for treadmill trimline 2600
- m sand machine imbatore in madras tamil nadu south africa
- ball mill balls suppliers in chennai
-

Primary mobile crushing plant

Independent operating combined mobile crushing station
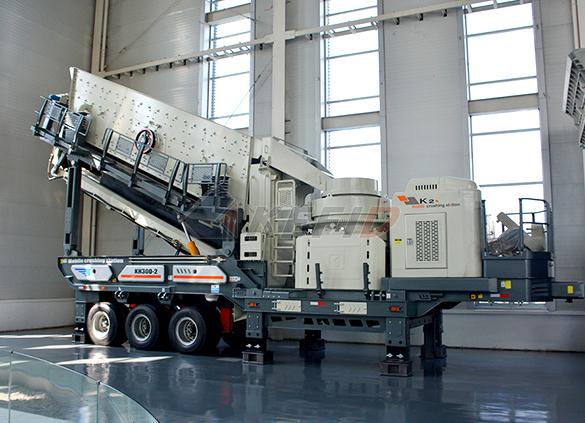

Mobile secondary crushing plant
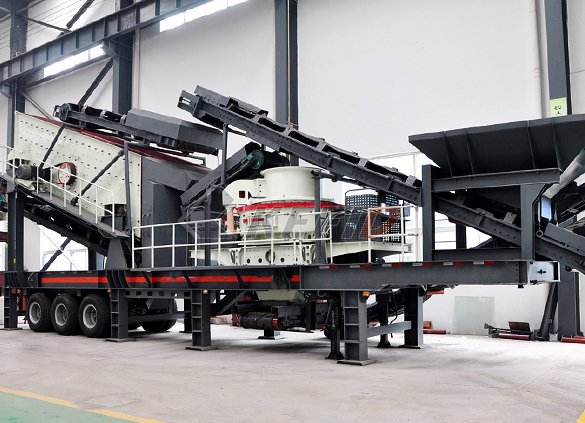

Fine crushing and screening mobile station
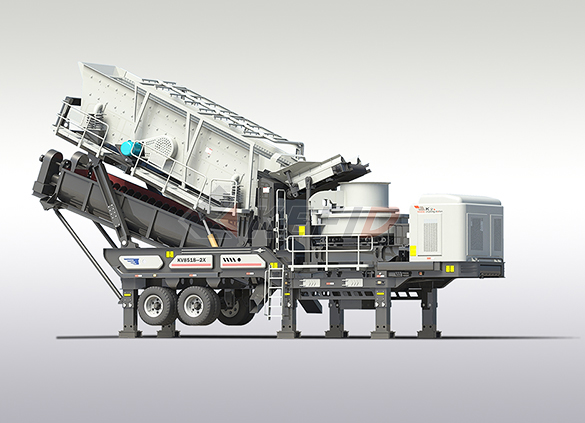

Fine crushing & washing mobile station
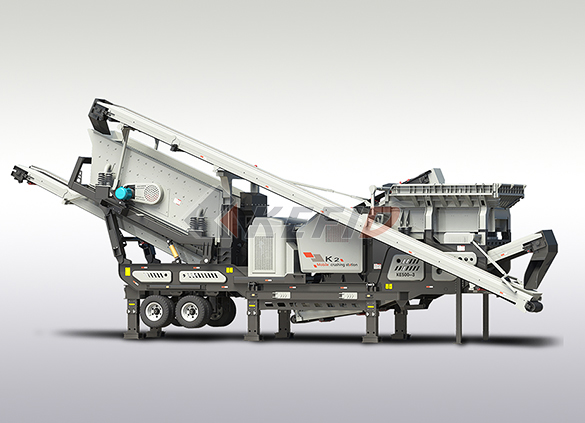

Three combinations mobile crushing plant

Four combinations mobile crushing plant
-

HGT gyratory crusher

C6X series jaw crusher

JC series jaw crusher

Jaw crusher

HJ series jaw crusher

CI5X series impact crusher

Primary impact crusher

Secondary impact crusher

Impact crusher

HPT series hydraulic cone crusher

HST hydraulic cone crusher

CS cone crusher

VSI6S vertical shaft impact crusher

Deep rotor vsi crusher

B series vsi crusher
-

Vertical grinding mill

Ultra fine vertical grinding mill

MTW european grinding mill

MB5X158 pendulum suspension grinding mill

Trapezium mill

T130X super-fine grinding mill

Micro powder mill

European hammer mill

Raymond mill
Ball mill
-

GF series feeder

FH heavy vibrating feeder

TSW series vibrating feeder

Vibrating feeder

Vibrating screen

S5X vibrating screen

Belt conveyor

Wheel sand washing machine

Screw sand washing machine

